All Content
All Content
Emily helps understand what hazard ratios are, what they can tell you about risks of a specific treatment, and how other factors like all-cause mortality also need to be considered when deciding on treatments.
By Emily KaplanEmily delves into the world of randomized clinical trials, explaining the steps in the process, the limitations of the trials, and common problems.
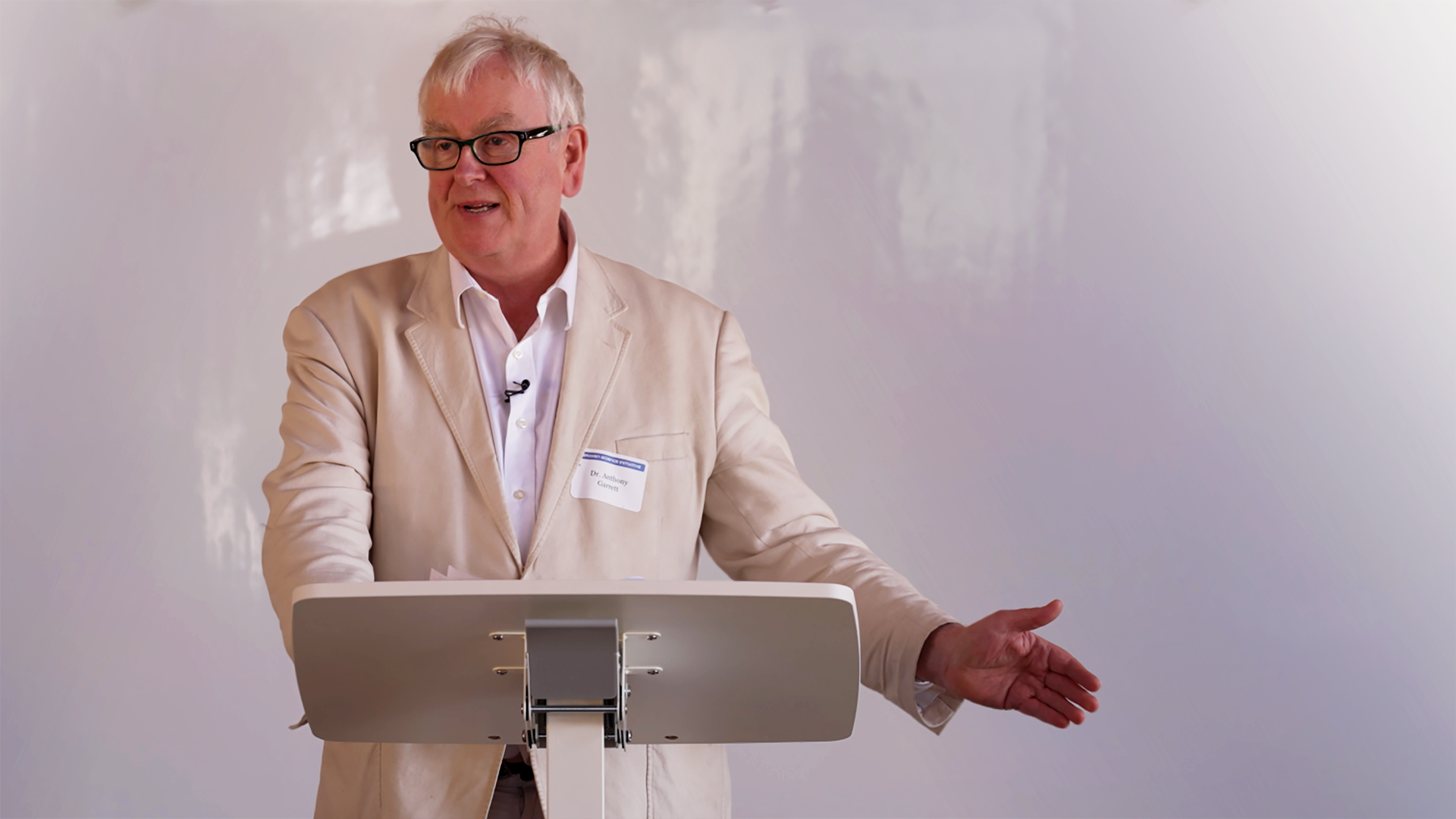
By Emily KaplanAnthony Garrett delivers a comprehensive lecture, touching on several major themes centered around the principles of probability, scientific methods, and the philosophical underpinnings of science.
A London librarian has analyzed millions of articles in search of uncommon terms abused by artificial intelligence programs.
Gerd dives into the history of statistical analysis in his field of psychology, which has led to a paradigm of rituals, in place of meaningful thought.
Frequently unreported or classified under a different cause, deaths from prescription drugs are on the rise. Peter Gøtzsche tallies up the totals and finds the risks to be higher than previously thought.
Malcolm elaborates on the power to manipulate studies when placebos are not benign.
Despite the expansion of the field of cancer genomics, Thomas Seyfried maintains that the metabolic view offers a better explanation for the cause, and better solutions for the treatment of cancers.
Big Soda has a history of cleverly concealing their influence in the health and fitness space by funneling sponsorship through proxy organizations.